
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born on February 22, 1857, in Tunisia, but his family origin is from Hamburg, Germany; Hertz is a celebrated physicist who is well remembered for his work on the electromagnetic spectrum.

Hertz decided to follow a combination of engineering and physics with the help of a doctorate received at the University of Berlin. These turn marked the beginning of profound advances in the field of electromagnetic theory.
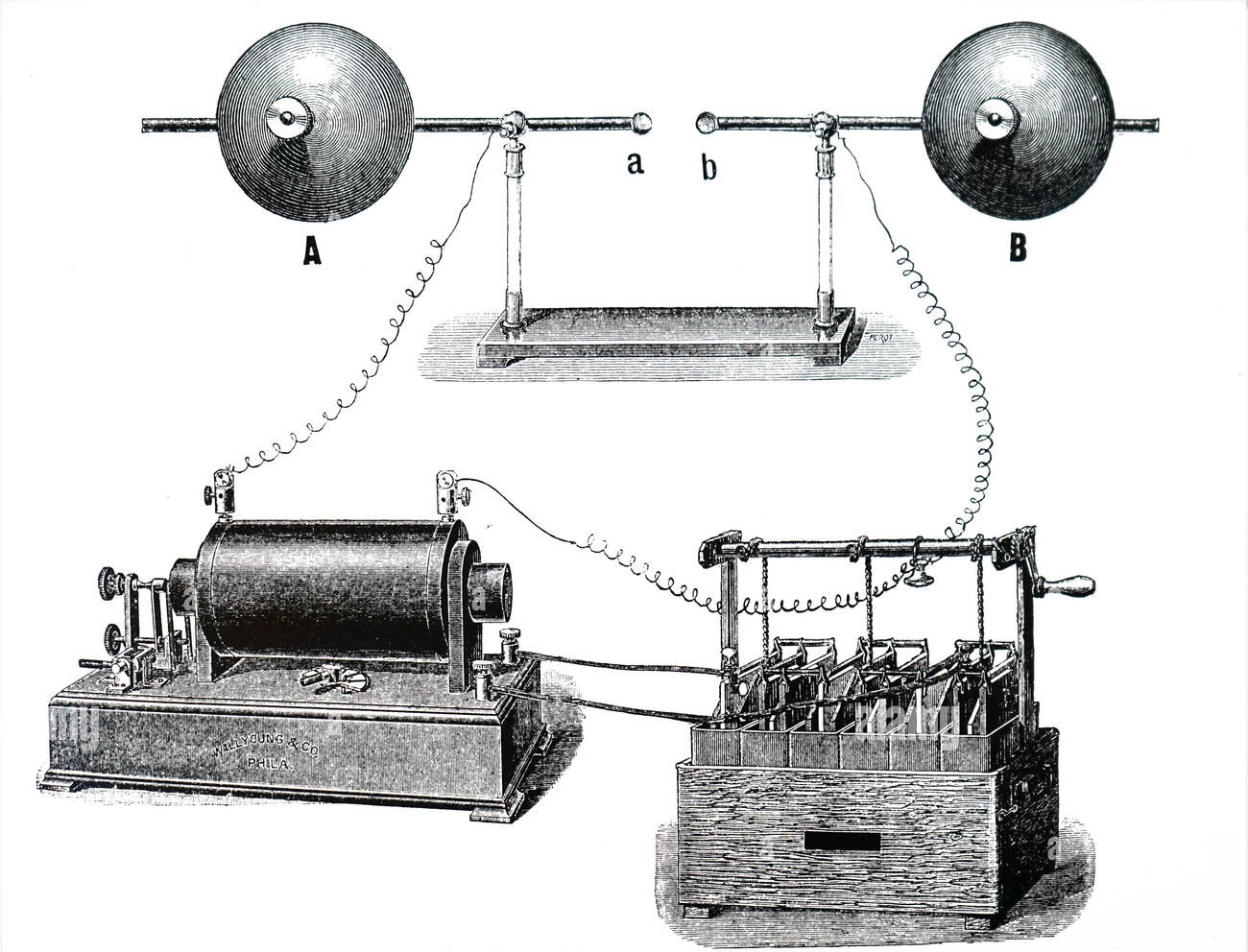
Thus inspired by the spirit of curiosity Hertz started specializing in engineering and physics in order to do his doctorate in the University of Berlin. This period can be characterized as a start of his achievements in the field of electromagnetic waves.
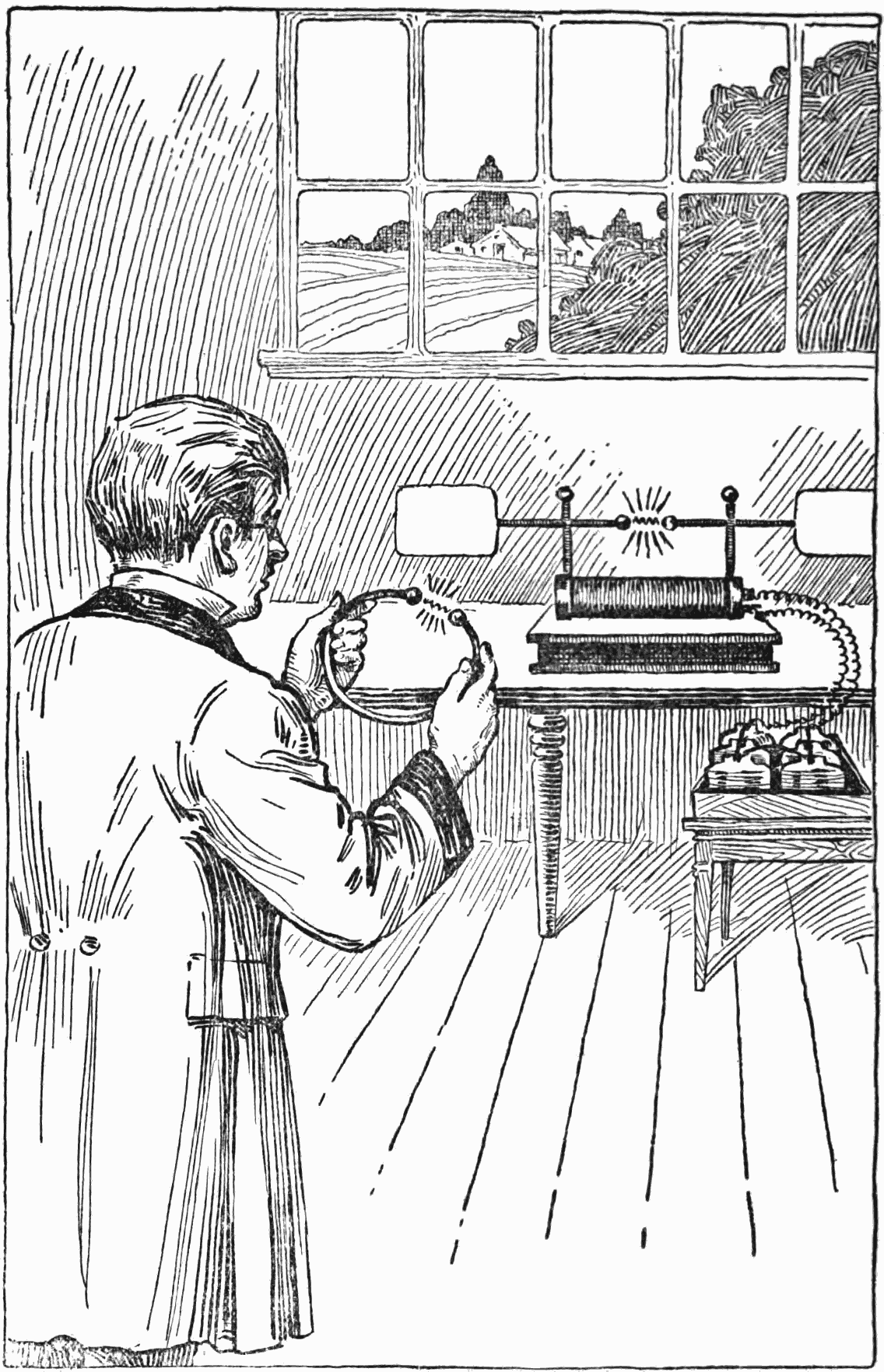
At the turn of the decade of the 1880s, Hertz gained scientific acclaim when he discovered that Heinrich’s Rudolf Hertz Empirical proof of electromagnetic waves theory advanced by Maxwell, James Clerk was true. James’ experiments confirmed Maxwell’s theoretical context hence expanding the knowledge about electricity and magnetism.
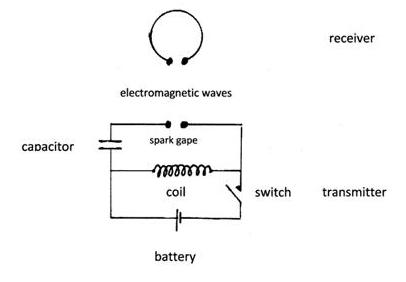
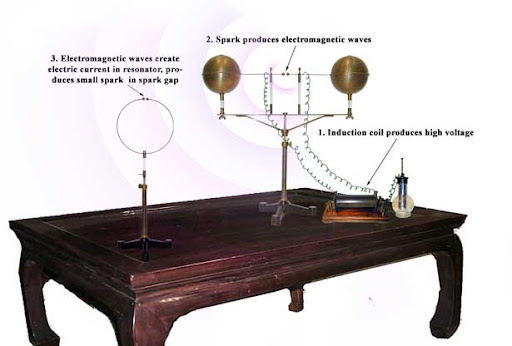
Although Hertz’s principles are not directly associated with the space, they laid out the framework for using radio communication technologies, which is critical in space missions.
At Hertz, Nagel’s inputs receive much acknowledgment. He was extremely young when he died at the age of 36 but his work has not been forgotten. His contribution to science is honoured by naming the unit of frequency, hertz.
Hertz was also a man of hard working and humble character. His passion for knowledge is evident and his impact saw the hertz coined in his honor.
Heinrich Hertz’s contribution is so fundamental that cannot be described not only by saying that it set the foundations of modern physics and technology. Fortunately, his experiments went down in the annals of history as having given birth to the contemporary methods of communication hence making him an important icon in scientific discoveries. As we saw in this case, his life was so short but his discoveries are still shaping the science and technology of the tomorrow.